Quadratic Relationships Dhaval Patel MPM2D0-F
Introduction To Quadratics
Introduction To Paroblas
-
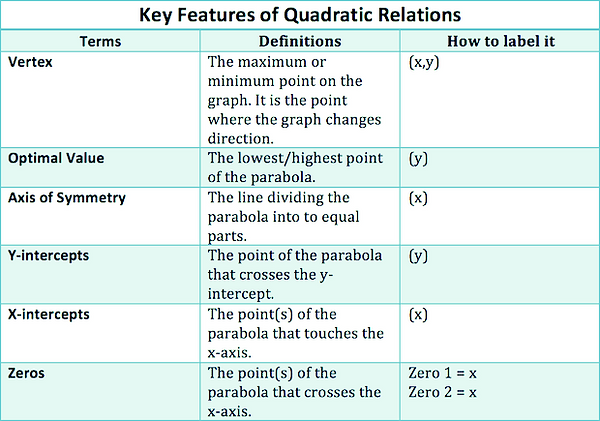
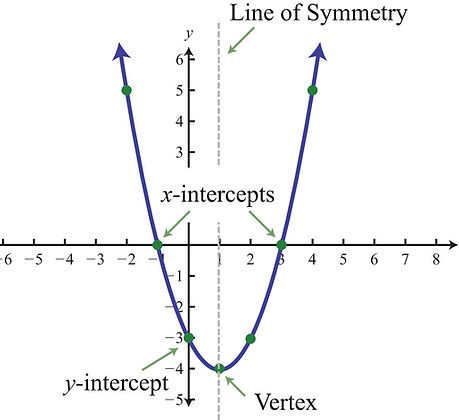
A parabola can either open up or down.
-
The zeros of a parabola is where it crosses the x-axis
-
The Axis of symmetry divides the parabola into two equal parts
-
The vertex of a parabola is the point where the AOS and the parabola meet.
-
The vertex is a y-co-ordinate which is optimal value
-
The y-intercept of a parabola is where the graph crosses the y-axis
-
The optimal value is the value of the y co-ordinate of the vertex
-
The vertex is the point where the parabola is at its maximum or minimum value.
Types Of Quadratic Equations

A quadratic equation is any equation having the form ax^2+ bx + c= 0
Where x represents an unknown value , and a, b, and c represent known numbers such that a is not equal to 0.
If a = 0, then the equation is linear, not quadratic. The numbers a, b, and c are the coefficients of the equation, and may be distinguished by calling them, respectively, the quadratic coefficient, the linear coefficient and the constant or free term.